If you’ve been researching the best projector for your office presentation or home cinema needs, there’s a high chance that you’ve frequently come across 2 main options: 3LCD vs. DLP. This is especially true if you’re browsing on a budget.
The DLP (Digital Light Processing) projector was launched in the late ’80s, while the LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) has been around since the 1960s. Despite both of them being launched pre-2000s, they still serve as popular projector options primarily due to their functionality and affordability. If you’re unsure of the differences between the 3LCD and the DLP, you’re not alone. Most users have a hard time differentiating the two.
This article will walk you through 3LCD vs. DLP to help you choose the best option based on your needs. Each projector has a distinct set of pros and cons, and your purchasing decision should be entirely based on your requirements.

The LCD landmark technology was first released in the 1980s, after which Epson refined and perfected the tech, launching 3LCD projectors in 1988. The first 3LCD model was the Epson VPJ-700 which was released for use in 1989. Many more models have been released after this, and even though Epson still owns the 3LCD tech, another organization is responsible for marketing this technology. This ensures that it’s not only Epson that makes the 3LCD projectors and allows members of the 3LCD consortium to use it.
One of the main reasons why most users prefer this projector type is its exceptional color output and amazing detailing of the images. Despite its technology being more than 3 decades old, the 3LCDs ability to offer the correct levels of brightness without using too much power remains unimpacted. It’s also an excellent option for Ultra and Full HD resolutions, making it the main competitor of DLP projectors. It is still sold in mass quantities.
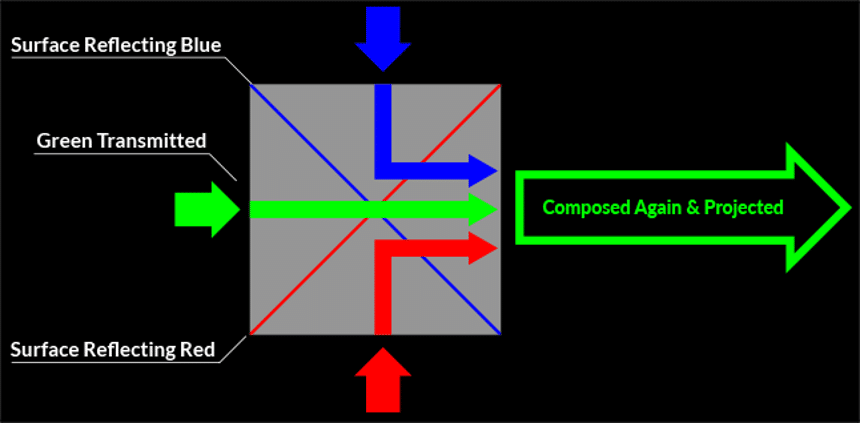
Images are created using a prism as opposed to a color wheel and tiny mirrors. The prism separates the LED or lamplight into 3 primary colors; red, green, and blue, which are commonly referred to as RGB. All RGB elements go through a specified LCD panel before being shown as colored images. Images are shown in color only after the separate colors are combined by the projector. This lack of a color wheel eliminates one of the most annoying elements of projectors; the rainbow effect.
According to most reviews, the Epson EpiqVision Mini EF11 is one of the best 3LCD projector models. It has amazing picture quality that delivers immersive viewing experiences and allows you to connect to your preferred streaming service provider. This 3LCD projector also offers outstanding audio quality due to its dual speaker audio system and comes in a simple but elegant modern design. The manufacturer offers lifetime technical support, a full-unit replacement, and a 2-year limited warranty.
The main advantages of using a 3LCD projector are:
3LCD projectors are also very popular among the DIY community and hobbyists.
Most LCD projectors, including 3LCD, are generally vulnerable to internal dust, which interferes with the quality of their image projection. They also have a more complex light path which can sometimes cause optical misalignment. Not unless you use an LED light source, you’ll have to replace the top lamp in addition to the filter cleaning that’s regularly required.
You should also note that after 3LCD projectors are used for over 9,000 hours, the prioritizer degrades, resulting in poor image quality. This occurs even when you use an LED as your light source.

Despite LCD being one of the modern projection technologies, DLP projectors still dominate a significant portion of the market and have a high sales rate. They’re also more affordable, which is why they’re used in conference rooms, schools, and colleges. They’re, however, costly to apply to HD technology.
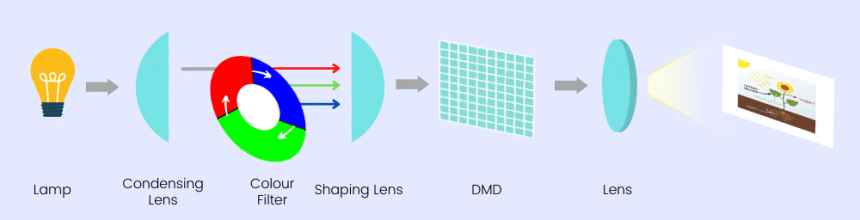
DLP projectors have micromirrors for each pixel. They bounce light from the source of a chip that contains these mirrors reflecting images from it onto the spinning color wheel, which then gives it the Red Green Blue tint. This process happens very quickly and alternates RGB & monochrome images, combining them to form one colored image.
According to most reviews, the Optoma HD146X is one of the best DLP projector models. Its installation process is fairly easy, and it’s flexible enough to be placed in any type of environment. It also produces crisp, HD images that have a cinematic quality and uses the latest technology from the manufacturer to eliminate image misalignment. The Optoma HD146X has a games mode that features a fast response time and allows for lights on viewing. It also has a long lamp life and allows for HDMI and USB power supply.
The main benefits of DLP projectors include;
Due to the above benefits, DLP projectors have a large market share for mobile display projection systems as well as front projection devices.
Since DLP projectors use a spinning color wheel, it reduces the usability of the device once it gets worn out. Most people perceive the sequential color illumination of DLP technology as colored images, but there are some people who experience the rainbow effect. For some, these colored shadows can cause a psychedelic effect.
DLP projectors sometimes experience light leakage causing a light reflection off the edges of the micromirrors. This can, however, be solved by creating black borders around the projector screen. These projectors also have a lower light output compared to 3LCD and are slightly more expensive.

For instance, even though both projection technologies offer an impressive visual output, the quality of the images is different. This is why their preferred use varies, with DLP projectors being most suitable for casual games and home entertainment. These projectors also work well in dark or indoor settings and can be used in office conference rooms. LCD projectors, on the other hand, provide an all-around performance and are mostly suitable for presentations. They also work perfectly in both outdoor and indoor settings, thanks to their high brightness levels that effectively counter ambient light. If you’re, however, able to control the set-up area’s ambient light, you can go for a DLP projector.
You should also note that 3LCD projectors are usually limited to particular resolutions, while some DLP models offer 4K resolution. This, however, impacts their pricing, with 3LCD models being more affordable. DLP models also have a rainbow effect, but 3LCD projectors require regular maintenance and are prone to internal dust, which causes image misalignment.
Projection technology has come a long way, and according to BBC Trusted Source Laser projectors promise to deliver brighter 3D films This week for the first time ever a cinema audience watched a laser-projected 3D movie at the same brightness as they would have seen the 2D version. www.bbc.com , the latest laser technology can be used to show high-quality 3D films. When it comes to choosing the best projector, most people have a hard time choosing between 3LCD vs. DLP projectors. Before you make a purchasing decision, you should consider various factors, including image qualities, durability, projection technology, and price. You should also analyze the benefits and potential drawbacks to determine whether the model you’re interested in will meet your needs.





