Alternators and generators are both designed to turn mechanical energy into electrical energy, though how they accomplish this task is quite different. This isn’t the only thing about these two devices that isn’t the same, either, since they are used for different purposes, plus vary in efficiency, output, and many other factors.
For those who have never used one of these or taken the time to look into what they do, the difference between them can be somewhat confusing. That’s why it’s important to compare a generator vs alternator since this will ensure that you’re getting the right one for everything you need to power. If you’re interested in what these two devices have to offer, check out the following sections for more information.
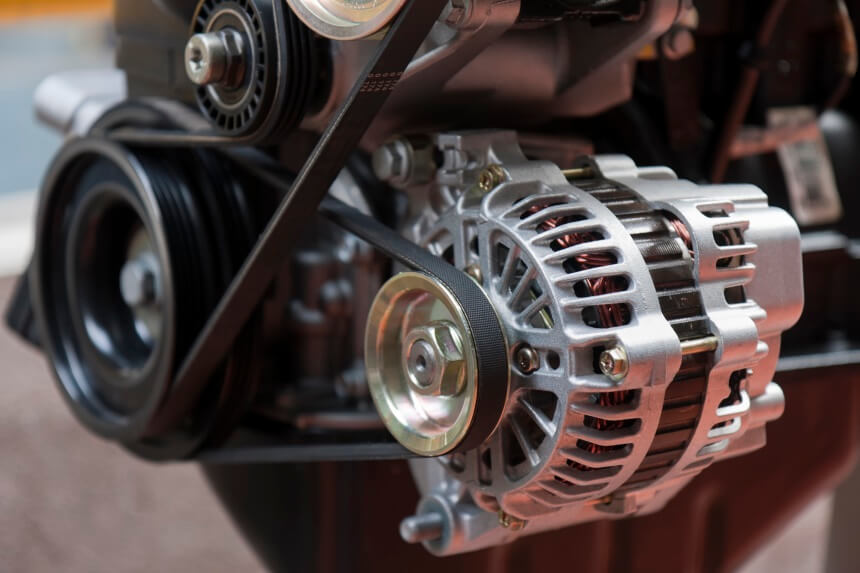
In your car’s engine, there is a drive belt that is resting on a pulley, which is attached to the alternator. When you start the car’s engine, the rotor shaft in the alternator is turned by the pulley, which then spins the magnets around a coil.
When these magnets spin, they create alternating current, or AC, which goes from the coil to the alternator’s rectifier, which is the piece that turns the AC power into the direct current, or DC, that is needed to activate all of your vehicle’s electrical systems. Modern alternators are designed to last a lifetime, as the Premier Gear PG-11311 Alternator proves, offering consistent performance and extra protection against excessive charging or failure.
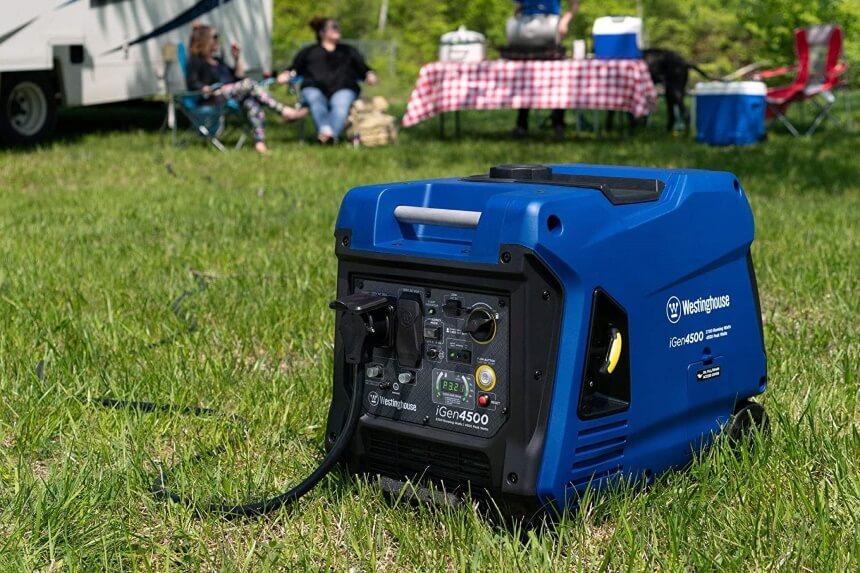

Generators Trusted Source Electricity explained - How electricity is generated An electric generator is a device that converts a form of energy into electricity. There are many different types of electricity generators. Most of world electricity generation is from generators that are based on scientist Michael Faraday’s discovery in 1831 that moving a magnet inside a coil of wire makes (induces) an electric current to flow in the wire. He made the first electricity generator called a Faraday disk, which operates on this relationship between magnetism and electricity and which led to the design of the electromagnetic generators that we use today. www.eia.gov are machines that supply backup power wherever you need it, including your home, camper, or business. Though you won’t use them often, they are a must during power outages to run the necessary items needed to survive, like furnaces, refrigerators, ovens, or lights. There are many different options to pick from, including the best whole house generators or smaller portable models that you can take with you wherever you need them.
Like an alternator, a generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, though it does so in a different way. A generator can also create both AC and DC energy rather than only one of them.
Inside the generator’s housing is a rectangular rotor that is made up of coiled wires, called an armature, which is rotating in a stationary magnetic field that has been created by either an electromagnet or a permanent magnet. This causes the magnetic field line that intersects the conductors to vary, inducing a current in the spinning armature.
Connected to the armature is a slip ring or a commuter. The slip ring features a full circular connection that can continuously transfer the electric current from the rotating shaft, which creates AC power. The commuter works a bit differently since it has 2 or more breaks between then, so it reverses the current’s direction after every half rotation, resulting in DC power.
Now that you know what these two products are and how they work, it’s time to consider the differences between an alternator and a generator. The following chart and sections can help you determine which one you need for any given situation.
| Generator | Alternator | |
| Energy efficiency | Less efficient | Highly efficient |
| Output current | Alternating or direct current | Alternate current |
| Energy conservation | Less energy conservation | More energy conservation |
| RPM | Low range | Wide range |
| Magnetic field | Stationary or fixed | Inside the stator |
| Size | Wide range of sizes | Small models |
| Fields of use | Large-scale electricity production | Automobile industry charger |
When you compare the current output of an alternator vs generator, there is a noticeable difference. Though both convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, an alternator then creates AC electrical energy, while a generator can convert the power to both AC and DC energy. This makes the generator a bit more versatile since it can power almost anything. Generators have a lower output current than alternators, though.
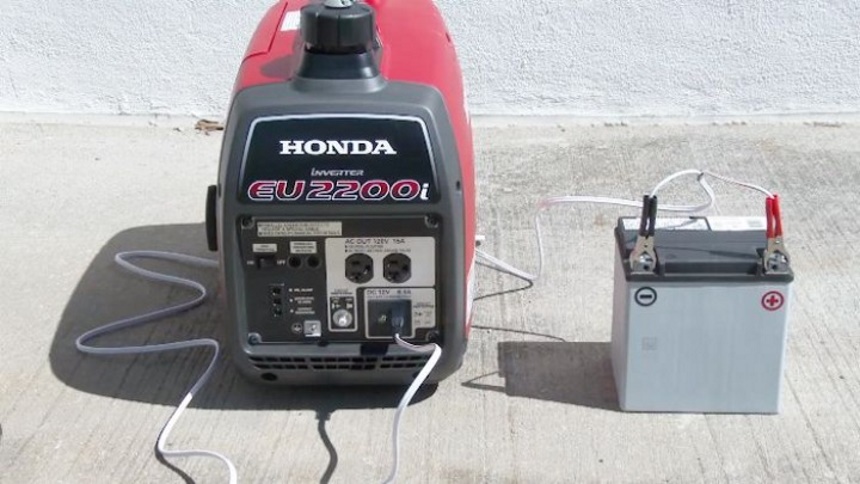

A generator is different. The best inverter generators, as well as the whole home or portable models, can all charge a dead battery, so you’re never stranded for long.
One of the biggest differences between a generator vs an alternator is the size and weight of these two products. An alternator is relatively small since it needs to be able to fit among the other engine parts in your vehicle to charge the battery when the engine is running. They are also lightweight and easy to carry around in one hand.
A generator is a much larger piece of equipment. There are some portable models available, like the Wen 56475 Portable Generator, which are smaller than the whole house models, but they are still quite large and can weigh over 100 pounds.
Products that are energy-efficient are more highly prized than those that waste energy since the latter cost you extra money while negatively affecting the environment. An alternator is the better option in this category since it conserves energy, only working when your vehicle is running and using only the required energy needed to keep the battery charged. Generators are the opposite, using up all of the energy that they produce rather than conserving any of it.

Alternators vary in price, depending on the type of vehicle you own. They can run anywhere from $180 to over $1000, though the average price you’ll pay is usually about $500. These pieces are designed to last a long time, so you will likely need to purchase one at the most for your vehicles and often none at all.
Generators are much more costly, though the prices can vary between the inverter, whole-home models, and portable models. Depending on the size of the generator and how much it can power at one time, you could be spending anywhere from $275 to well over $15,000 for one of these models.
How these two products generate power is another important difference to consider. In an alternator, the magnetic field is spinning inside a coil of wires to create the current. When it comes to a generator, it is the opposite, with the coil of wires rotating inside of the magnetic field. This difference in how they produce power allows alternators to run at much higher speeds and they can produce more power than generators at lower speeds.
When it comes to the RPM range, there is another significant difference between alternators and generators. An alternator has a much wider RPM range, while a generator has a low RPM range with only slight variations.
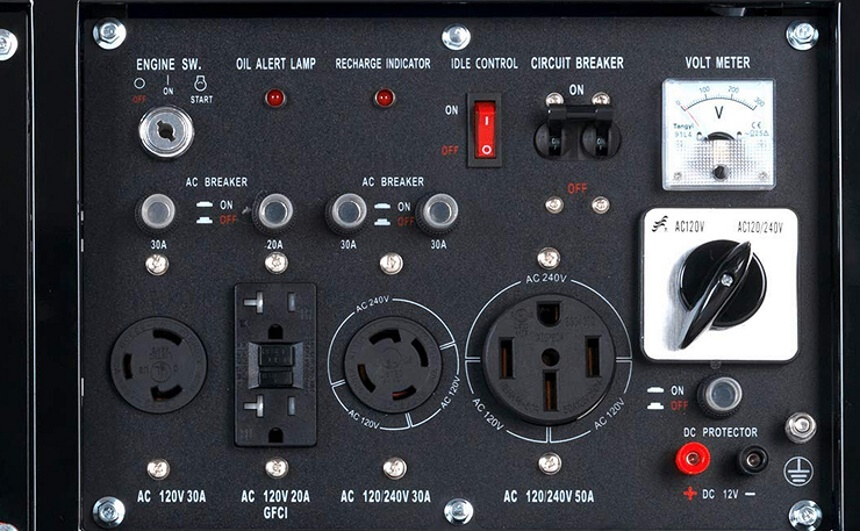

Wheels are often included on the portable generators to make them easier to move, though this isn’t always the case. If you plan to move your generator around, this is another feature to consider.
A low-oil shutoff is another great feature to ensure that the generator doesn’t keep running when it runs out. You may also want to consider the best dual fuel generator since these allow you to use both gasoline and propane to power them.
A generator that includes plenty of outlets is also a must. These ensure that you can power multiple items rather than trying to run them all from a single outlet, which can be rather unsafe and even cause damage to the generator.
If you aren’t sure which one of these is the right one for you, let’s take a look at what alternators and generators can do for you and which one is best for any given situation.
Though both generators and alternators create electrical power, an alternator can’t do so on its own. It needs other engine parts to work properly and can’t even be used until the engine is running.
Alternators do have the benefit of being small, lightweight, and energy-efficient, plus they last longer and offer a higher output due to the faster rotations. This is why alternators are mainly used in vehicles to keep the battery charged.
Generators are much more versatile machines, with all-in-one systems that allow them to run independently. They can create both AC and DC energy, so they have more uses than an alternator.
Generators come in a variety of sizes, so you can get a large one to use as a power supply for your entire home or a smaller, portable model to power just one or two things, like charging your cell phone or giving your car a boost when the battery has died. These handy devices can also be used almost anywhere, including your home, a job site, a factory, or even to keep the power on in your RV when camping.
Though they both have the same basic function, which is to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy, there is a wide range of differences in how this is done when you actually compare a generator vs alternator. Alternators only generate AC energy, with a higher output and a wider RPM range. They are used mainly in vehicles to charge the battery, as long as there is enough juice to get the engine started.
A generator is an independent machine that can create both AC and DC, so you can use it to power your home during an outage, as well as at a job site or campground when you have no other power source. There are large or small models, so you can always get the right one to meet your needs.