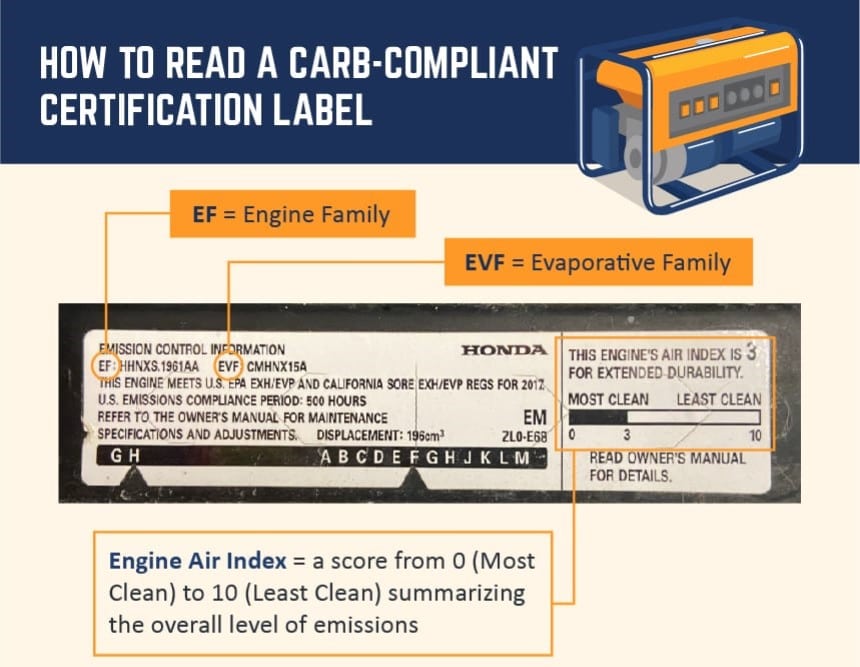
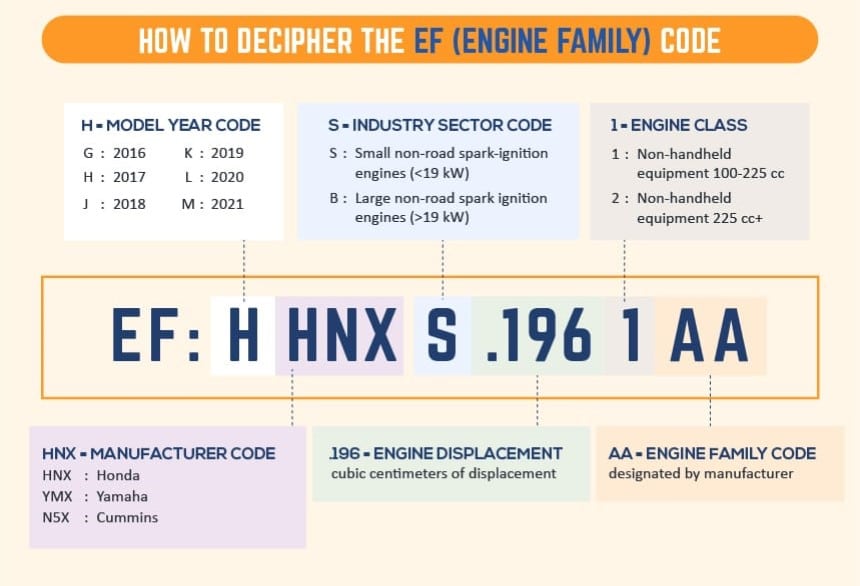
CARB and CARB-compliance are terms often found and used in the automotive and power equipment industries. So, what is CARB compliance, and what is a CARB-compliant generator? Well, as the world continues to struggle to adapt to a warming and pollutive planet filled with carbon emissions, as well as both noise and air pollution, CARB is the state of California and the United States’ answer to planet sustainability.
CARB’s mission is to help the State of California achieve and maintain a level of air quality that promotes good health for all and the environment; protect the public from exposure to unwanted or toxic air contaminants; providing, when necessary, innovative approaches to comply with air pollution laws and regulations. CARB regulations often apply to the manufacturing and distribution of generator equipment. A CARB compliant generator is that with a low level of noise and carbon emissions.
In this article, we’ll see what the term is and what a carbon compliant generator means.

It is the only Agency of this type in the country, since it was created a few years before the EPA (the federal agency, founded in 1970). This agency was created in 1967 by Governor Ronald Reagan after he signed the legal document known as the “Mulford-Carrell Act.” This saw the merging of the Office of Air Sanitation Bureau with the control board that monitors motor vehicle pollution.
California remains the only American state that is allowed to have a regulator like CARB as it was the only one that did when the federal Clean Air Act was passed. Other states are allowed to follow the standards set by the CARB, or use the EPA).
CARB has also played an important role in driving innovation in the US automotive industry, but also globally through programs such as its ZEV mandate. In 2015, it was (along with the EPA) one of the organizations that helped bring the Volkswagen scandal to the fore (it had embedded software allowing the results of laboratory pollution tests to be faked).
Vehicles and power equipment that are CARB compliant means they meet the standards of air pollution set by the CARB. This is not to say that they don’t produce carbon emissions at all, for example. However, CARB-compliant equipment emits less pollution than non-compliant generators. Therefore, a CARB compliant generator like the Westinghouse WGen7500, for example, operates under low noise (around 60 to 80 decibels noise level, generally) and makes very low dispersion of fumes which could result in the production of carbon monoxide, the so-called silent killing chemical found in an electric generator.
According to most reviews, one of the most popular CARB-compliant generators is the Pulsar G12KBN which is powerful enough for most applications, can run on gasoline or liquid propane and is transfer switch and RV ready.
 What if my generator is not CARB compliant?
What if my generator is not CARB compliant?Well, there is a limit to the states where you can buy or use electric generators that are not CARB compliant.
In California specifically, you cannot buy, sell, or use generators that are not approved by the CARB. However, many states in the country are adopting the standards and regulations of the CARB.
These states include Colorado, Connecticut, Maryland, Massachusetts, Delaware, Maine, New Jersey, New Mexico, Oregon, New York, Pennsylvania, Vermont, Rhode Island, Washington, and the DC.
Imagine that every morning in the aftermath of a hurricane, with no power supply, the cry of your son leads you to search with a flashlight for the therapy machine. In the dead of the night, you only have your car or your diesel generator which is the only way to turn on the equipment that neutralizes the minor’s shortness of breath. After turning them on, you jump back to bed.
Meanwhile, the environment is permeated with the fuel that allows your son to sleep pleasantly; when it is burned, it is converted into carbon monoxide, a potential killer that knocks people out in minutes. A scene similar to this, or worse, is repeated in thousands of homes every year.
Many localities smell and breathe diesel during the aftermath of Hurricane Irma, Hurricane Maria, and Hurricane Lamar. In many corners, the smell and noise of electric generators usually become a part of everyday life in affected regions.
Several weeks after the collapse of the power system, the government does not usually have a clear public policy for the prolonged operation of these power equipment, which are supposed to be used only in emergencies.
In the US, there are hundreds of thousands of electric generators, most of which operate with gasoline and/or diesel. Many citizens, by not hiring an expert, install them without taking precautions, putting their safety and that of their neighbors at risk.
For example, after Hurricane Irma in Orange County in Florida, three Puerto Ricans died from carbon monoxide emissions from an electricity generator in their residence.
During each hurricane season, hundreds of people are intoxicated with the carbon monoxide emanations from these devices, and tens of people die.
According to the Center for Disease Control (CDC) in a month, six people died and 167 were poisoned with carbon monoxide related to the use of generators in Florida after millions of inhabitants were without power after being hit by four hurricanes, between August and September 2004.
Hence, the improper use of high carbon-emitting generators could have lethal consequences. Every year in the United States, at least 430 people die from accidental carbon poisoning Trusted Source Carbon Monoxide (CO) Poisoning Prevention | NCEH | CDC Every year, at least 430 people die in the U. S. from accidental CO poisoning. Approximately 50,000 people in the U.S. visit the emergency department each year due to accidental CO poisoning. There are steps you can take to help protect yourself and your household from CO poisoning. Change the batteries in your CO detector every six months. If you don’t have a battery-powered or battery back-up CO detector, buy one soon. www.cdc.gov .
However, in recent times, many regulatory bodies granted a waiver to allow the use of electric generators without operating permits. However, citizens have tried to file complaints to denounce the illegal operation of electricity generators.
The positive response, however, is with the adoption of the standards on air pollution and regulations by the CARB in other states of the US.
The board of directors is made up of eleven members appointed by the state governor. Half of these members are experts in professional and scientific fields such as medicine (environmental health), chemistry, physics, meteorology, engineering, economics, or environmental law. The other members represent pollution control agencies from various regional districts in California.
CARB is organized into nine main levels or departments:
Recently, one of the first responses to CARB’s regulations is with the massive production of inverter generators and other low-emitting portable generators. These generators not only make low carbon emissions, but they are also now as quiet as possible. Hence, these make them more environmentally-friendly, which is why many of these generators are approved for use in residential places.
Because an electric generator does not come with CARB compliance or approval and EPA certification does not mean you can not purchase it. However, this only applies to those living or operating businesses in the state of California. Non-CARB-approved generators may be illegal to use in this state.
Although your choices may be limited due to these emission laws governing the use and sale of certain power equipment items, there are still however a large number of generating sets with compliance with these regulations on the market. However, you’ll still be surprised to find out that most of the big brands, some of which might be your favorite, are failing to comply with these regulations. So, for localized and updated information, ensure you check the websites and databases of your local municipality and the official website of the State of California before choosing to buy an electric generator.
Obviously, the greatest benefits of CARB-compliant generators are to the collective advantage of the planet. However, in the immediate environment, they help limit the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning and other health issues caused by high carbon emissions.
With CARB-compliant generators, users do not have to sacrifice environmental sustainability for back-up power in the event of an outage.
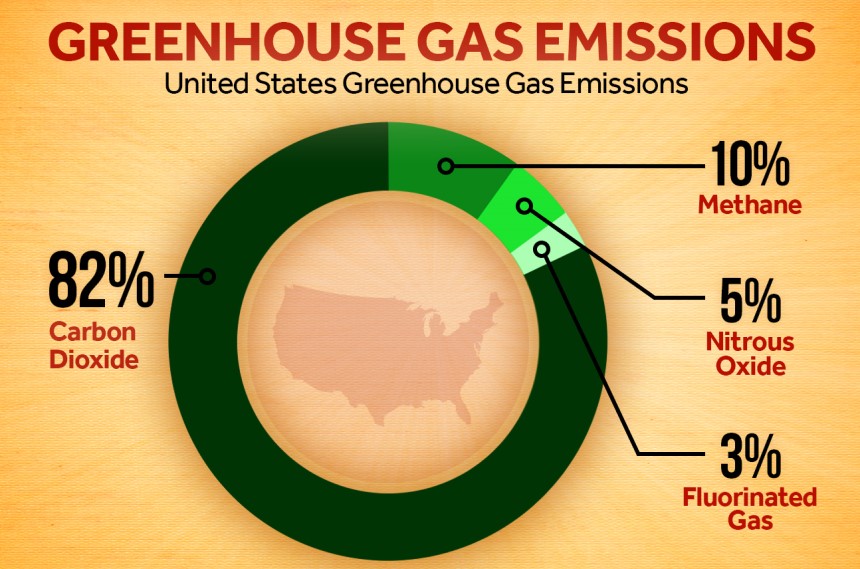
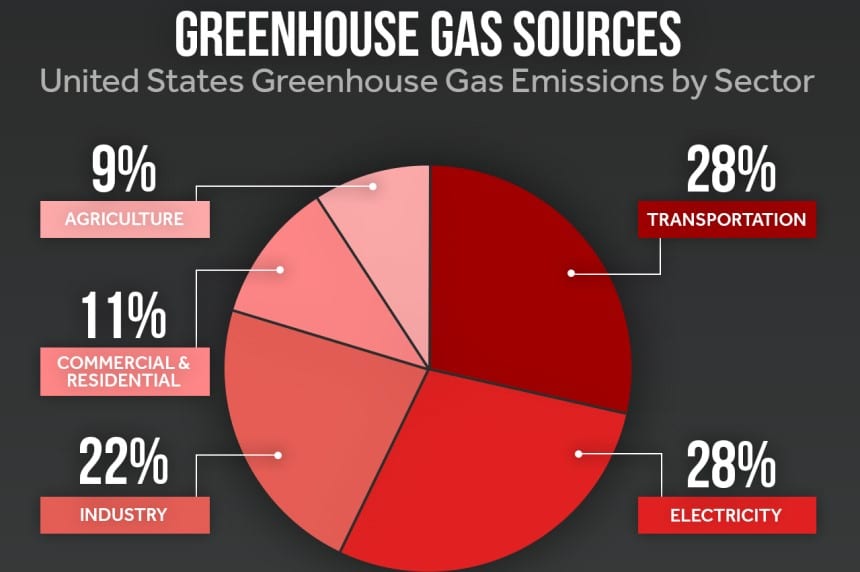
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon necessary for our survival. This causes an increase in the temperature on the surface of our planet. Our activity on Earth modifies the chemical composition of the atmosphere and leads to the appearance of an additional greenhouse effect, largely responsible for the disruption of the climate.
CO2 is the most common greenhouse gas emitted by power equipment. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the result of the combustion of fossil fuels, for example, diesel, petrol, and propane.
 The problem of carbon emissions
The problem of carbon emissionsThe increase in carbon concentration globally is primarily due to the dependency on fossil fuels and also land use. Carbon dioxide and global mean temperature are closely connected. If emissions and concentrations of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere increase, the global average temperature also increases.
The problem of the higher or lower concentration of carbon dioxide is a problem of higher or lower global temperature.
From the 1800s till today, but especially in the last half-century, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is increasing. As well as that of other greenhouse gases, in particular methane and nitrogen oxide. These gases are responsible for the greenhouse effect that acts on the mechanisms for maintaining the Earth’s temperature. But then, if greenhouse gases in the atmosphere increase, does the greenhouse effect become more efficient or hold more heat? And can this have consequences on the earth’s temperature?
To try to solve this question, we must first have data on the Earth’s temperature. It is easily measurable … since thermometers exist!
However, scientists, through ice, corals, trees, are also able to trace the temperatures present many years before the invention of thermometers. Having the temperature data, we can then investigate whether the average terrestrial temperature, such as the atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide, has also varied over time and, if so, if its variations are related to those of CO2. The global climate of our planet has undergone and is undergoing, in an increasingly evident and rapid way, a change that is not justified by causes internal to the climate system (orogenesis, epirogenesis, ocean current variations, etc.) or external to the climate system (astronomical: eccentricity of the Earth’s orbit, obliquity of the Earth’s axis, the precession of the equinoxes).
With respect to the natural carbon cycle, the human species, with the use of fossil fuels, does nothing but re-enter into the atmosphere – as CO2 – what nature, in millions of years, has subtracted and stored in colossal deposits underground. The growing anthropization of the planet and the change in land use also contribute to the increase in the atmospheric concentration of CO2, perturbing the climate through the re-release into the atmosphere of what the terrestrial biosphere had previously “sequestered” (soil processing and management, in general, cause a significant loss of carbon contained in the soil).
The role that the increase in greenhouse gases has in the ongoing climate change is now commonly accepted. There is a general consensus in the scientific world about the role of human responsibilities in bringing about climate change.
Over the past two centuries, the amount of CO2 has been increasing and in 2011 reached a concentration of 391 ppmv (parts per million by volume), value above the natural concentration range (180–300 ppmv) of the last 800,000 years and most likely of the last 20 million years. Compared to the pre-industrial period, it has increased by 40%! The annual increase is 2.0 ppmv, and it is higher than the average growth rate of the 1990s (1.5 ppm per year) while it is on average with the previous decade. Emissions are decreasing in Europe, while they are increasing in emerging economies. China and the US are today the world’s largest emitters.
Thermometric measurements have only existed for about 132 years. Temperatures from the more distant past are measured mainly by using substitute variables: sediments, pollen, and fossil shells, tree rings, corals, oxygen isotopes present in ancient ice. The results of these observations are reported in the IPCC reports which clearly shows how in the twentieth century there was an average climate warming of 0.74 °C over the last 100 years (1906–2005). This is unprecedented in the rest of the millennium either in terms of growth or duration.
The IPCC, based on various scientific evidence, concludes that the warming has not been constant over the years. Much of the increase is concentrated, in fact, in the last 50 years, the warming trend is around 0.65 °C (0.13 °C per decade) while it was “only” 0.09 °C in the first 50 years of the century (1906–1956). Furthermore, of the 12 years between 1995 and 2006, 11 have been classified among the hottest ever recorded since the birth of modern meteorology (from 1850).
An average household in the US produces, on average, 7.5 tons of carbon per year Trusted Source Forest Preserves The average US household produces 7.5 tons of CO2 equivalents per year. Here are things you can do to help reduce that amount. www.ccfpd.org , according to the CCFPD.
However, this situation changed as generations Z and millennials grew and became more aware of the impact generated by the overwhelming levels of consumption. Although it still remains in the red, now young consumers are willing to pay more for products that represent their values and have less impact on the environment in which we live.
Hence, more and more organizations are concerned with making brands and products that are sustainable and friendly to the environment, because apart from favoring a positive impact on the planet, now this has become a way to generate income responsibly.
These are some of the benefits that organizations could have if they worry about reducing the CO2 emission generated by their production days.
Some of the leading brands with a wide line of CARB-compliant generators are Champion Power Equipment and Westinghouse. They have popular models as this 3500-watt portable generator, which proved to be fuel-efficient and user-friendly thanks to remote control, an RV-ready outlet, and other features, as well as the Westinghouse WGen7500 with 9,500 maximum watt power and transfer switch-ready design.
When facing the measures that will be carried out in the medium and long term to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to combat climate change, the debate usually turns to the cost of transforming the energy sector. A study published in Nature Climate Change considers that this approach is limited because it ignores the human cost of delaying the implementation of measures to reduce these polluting emissions.
The key, according to the study led by Duke University (North Carolina, USA) is for governments to accelerate their calendar to reduce fossil fuel emissions instead of postponing major cuts, as some governments have proposed.
The research points to the need to advance the commitment during the Bonn climate summit. The nearly 200 countries that attended the meeting agreed to keep the planet’s temperature rise below two degrees, and if possible, limit it to 1.5 ºC.
City by city, the study looked at the number of lives that could be saved in 154 of the world’s largest urban areas if emissions reduction measures are accelerated and global temperature rise is limited to 1.5 degrees Celsius in the short term.
 Asia and Africa the biggest beneficiaries
Asia and Africa the biggest beneficiariesThe study estimates that up to 153 million premature deaths related to air pollution such as carbon monoxide from generators could be avoided worldwide. Asia and Africa would be the continents that would benefit the most. As for cities, Calcutta and Delhi in India top the list with up to 8.4 million lives saved between the two cities.
A total of 13 Asian and African cities could prevent one million deaths each, and about 80 cities worldwide could prevent at least 100,000 deaths. Sao Paulo, Los Angeles, Moscow, New York, and Mexico City, among others, would potentially prevent between 320,000 and 120,000 premature deaths each.
In Africa, carbon monoxide poisoning from generators and other sources kills 600,000 people every year. However, with campaigns, policies, and regulations to cut carbon emissions of power equipment and plants, these numbers are bound to reduce if regulation standards are adopted.
The study states that deaths would be reduced in cities on all inhabited continents, but especially in Asia and Africa with carbon emissions. Assuming that it is feasible for CO2 emissions and associated air pollutants to remain at higher levels in the short term, in the hope that they will be offset by negative emissions in the future, is a very risky strategy. It is like buying something on credit and assume that one day you will have an income large enough to pay for it all.
From Duke University, there is the hope that this information will help politicians to take advantage of the benefits of accelerating carbon emission reductions in the short term, raising awareness by showing the enormous benefits that can be obtained for public health, in addition to the mitigation of the effects of climate change.
The CARB and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) are two of the most trusted organizations when it comes to certifications of products that are sustainable to the environment. Both endorse the energy efficiency and the environmentally-friendliness of power and environmental products. However, while EPA regulations cover all parts of the US, CARB regulations only cover the state of California, although many states have begun to adopt the board’s standards.
СARB compliance is often stricter than EPA’s standards on emissions. This is why CARB-compliant generators are more acceptable and attractive to consumers.
New generation consumers are willing to pay more for products that represent a more sustainable lifestyle, it has been established.
The environmental impact generated by the goods and services production industry has set the trend in recent years. The changing dynamics of consumption and the accelerated appearance of new needs produced by the difficult conditions that humanity has been dealing with have put different industries to produce at the top of their capacities. And one of the new demands by consumers of power equipment in the event of outages is CARB compliance. The standards set by the Californian agency has made its certification more commonly looked out for in electric generators. We hope you now know what is CARB compliance and that by now, to save our planet, save human lives, and live a healthy life, you would prioritize CARB-compliant electric generators in conditions that require that you operate off the grid.