First and foremost, using a spin bike has a higher risk of injury than a stationary bike does. So, especially if your body isn’t used to regular exercise, a stationary exercise bike is your best bet. Using a spin bike also burns more calories than a stationary one and also typically works more parts of your body. A stationary exercise bike will work your quads, glutes, hamstrings, and calves, while a spin bike works all of those in addition to your shoulders, triceps, core, and back.
Taking a spin class can get expensive, so if you’re dedicated to it, buying your own spin bike is a much better investment, and it will pay for itself very quickly. Depending on your budget, you have a lot of options. If you’re willing to spend up to $1000, these options are some of the most reputable. If your budget is a little slimmer, there are also some great choices for less than $500. You’re not without options if neither of those price points is suitable for you, though. You can find some highly rated spin bikes for less than $300 as well. If a spin bike isn’t for you and you’re looking for a simpler workout, plenty of stationary bikes are out there for competitive prices. You can even find them on Amazon, and of course, there are options for those with tighter budgets as well.

The main difference between the two is that a spin Trusted Source Health Benefits of Indoor Cycling: A Systematic Review - PMC Results revealed that indoor cycling may improve aerobic capacity, blood pressure, lipid profile, and body composition. These enhancements may be achieved as standalone intervention or combined with other physical exercises or diet. Conclusions: The combination of indoor cycling and diet is recommended to improve the lipid profile, lose weight, and reduce blood pressure. Furthermore, indoor cycling alone may also enhance aerobic capacity. Given the lack of randomized controlled trials, these conclusions should be taken with caution. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov bike gives you a higher intensity exercise, while a stationary bike is a low impact. The most common use for a spin bike is something most people have heard of by now—spin classes. A teacher will lead a class and guide people through different intensities and movements to work their entire bodies. But this doesn’t mean you need to be in a spin class to own a spin bike. If you’re new to it, there are plenty of workouts online. The primary uses of spin bikes are usually to get in a low-impact workout that’s easy on your joints and body. It can be used as a warmup to get the heart rate up or as a slightly more impactful workout than walking. If you’re at home, a stationary or spin bike is a great pick for those who want to get their steps in but don’t have time to go back and forth from a gym. You can put on a show or movie and get biking, making time for multiple hobbies at once.
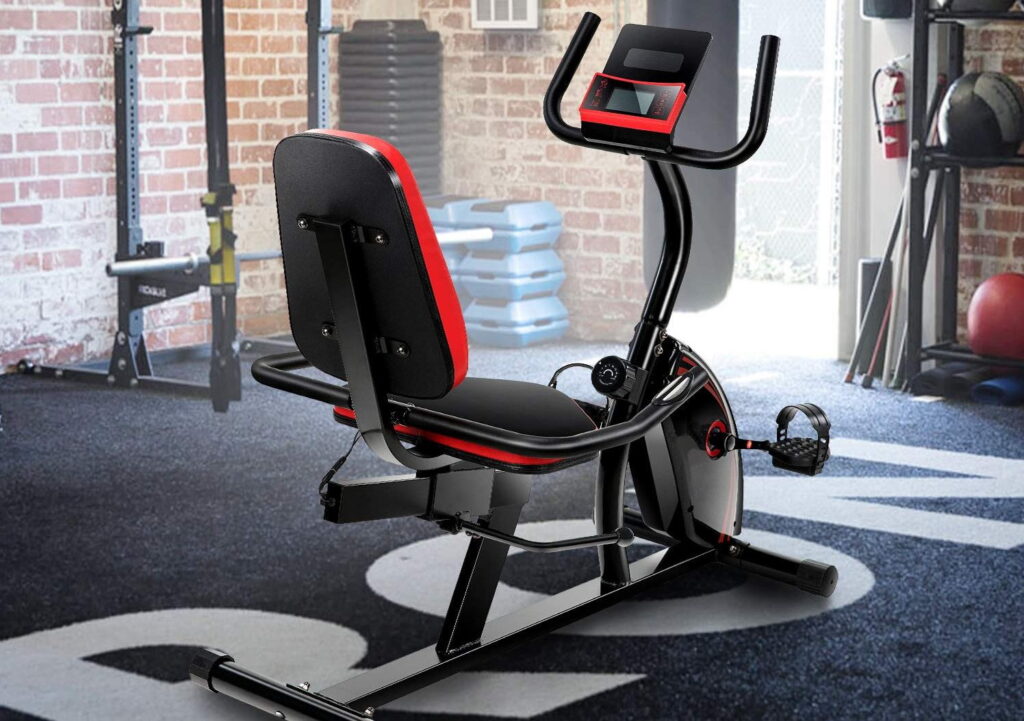
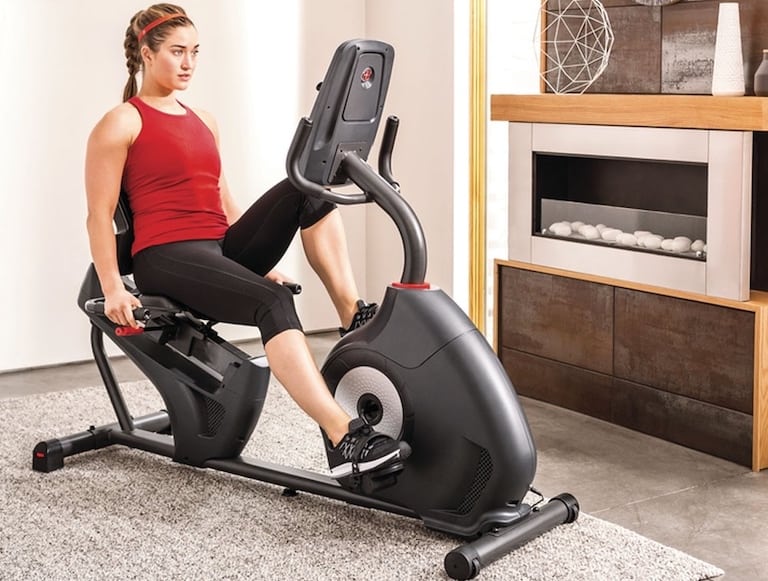
Stationary exercise bikes are primarily used for people who need exercise that’s easy on their joints. Anyone can use one, of course, like spin bikes, and you can adjust how you use it to get a more intense workout. Exercise bikes are easily found in the gym by the treadmills, whereas spin bikes will usually be in their own room at the gym, with an instructor present.
The easiest bike to use is definitely the stationary bike. It’s like a regular bike, but, well, stationary. It’s a pretty low-intensity workout, so you likely won’t find yourself dripping in sweat the way most people do with a spin bike. If you know how to ride a regular bike, you won’t have much of a problem with either. Spin bikes are usually much heavier and larger than stationary bikes because they have a flywheel that can weigh up to 20 pounds. Because of this design, they’re much harder to move than a stationary bike. Stationary exercise bikes are much lighter, and in some cases, they can be foldable. Spin bikes are meant for shorter, higher impact sessions, so the seat on a spin bike tends to be harder and less comfortable than that of a stationary bike.
Sitting on a spin bike doesn’t have much injury risk but standing on one might. Particularly because spin classes get intense and fast, and with this range of movements, you’re at a higher risk of injury. You’re likely to get a sore back due to being hunched over. But a stationary bike has relatively no injury risk. Neither have considerably serious risks, especially if you don’t have any pre-existing injuries, but the injury risk of a spin bike is certainly higher than the risk of a stationary bike.
Using a spin bike for half an hour can burn anywhere from 400 to 600 calories. Of course, this depends on the intensity of your workout, as spin classes can range in speed and movement. Using a stationary bike for the same amount of time burns about half the amount that a spin bike does. Obviously, the more you bike, the more calories you’ll burn, but it seems that spinning will burn more calories than biking on a regular stationary bike because of the high intensity.
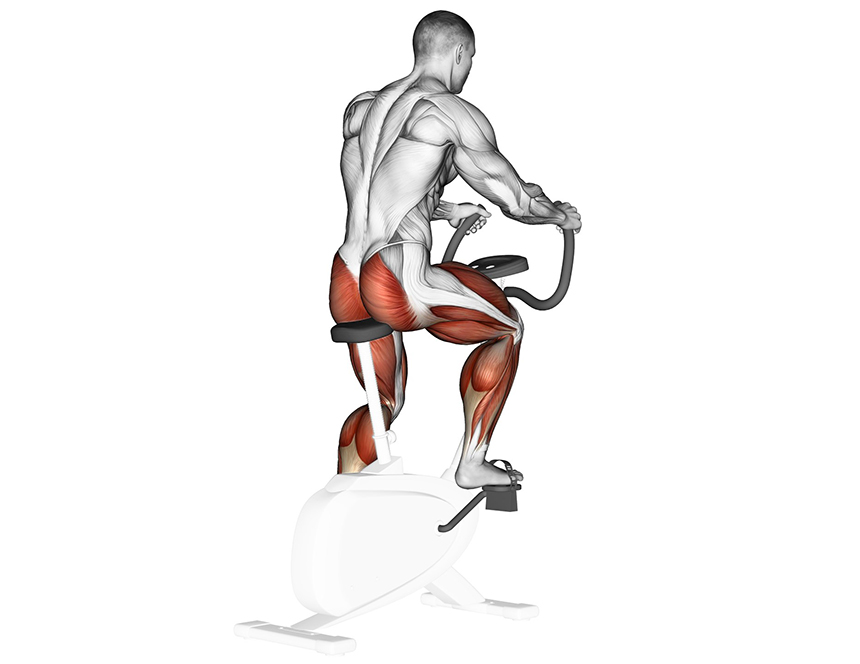
Using a spin Trusted Source Effects of 16-week spinning and bicycle exercise on body composition, physical fitness and blood variables of middle school students - PMC Body composition, physical fitness (1,200 running, sit-ups, back strength, sit and reach, side-steps) and blood variables (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, glucose, reactive oxygen species, and malondialdehyde) were examined before and after 16 weeks of training. As the results, body weight did not show any significant difference; however, body mass index, and % body fat were significantly difference in spinning group. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov bike engages 90% of these muscles. Whereas with a stationary exercise bike, the muscles engaged are only your lower body (i.e., glutes and legs). Spinning can be considered a full-body workout due to its intensity.
There are multiple positions taught on a spin bike, varying in the intensity that they work your upper body and the traction you will gain in your legs. This gives more room for progress in the sense of the amounts of different workouts you can do. A stationary bike typically has one movement, sitting down and moving the petals. You can also stand up on a stationary bike to get a more intense workout and engage your core.
The models of the different types of bikes are similar, though. They usually both have options to change the resistance and speed, so you can progress and regress your workout as you please and find what works best for you instead of being stuck on one resistance or speed.
Most spin bikes don’t come with a console in the middle that tracks your distance traveled and calories burned, whereas modern stationary bikes do. Of course, nowadays, there is another way to track these factors, like with a fitness watch. But if the factor of having a console that tracks your progress is important to you, be sure to consider it when making your decision.
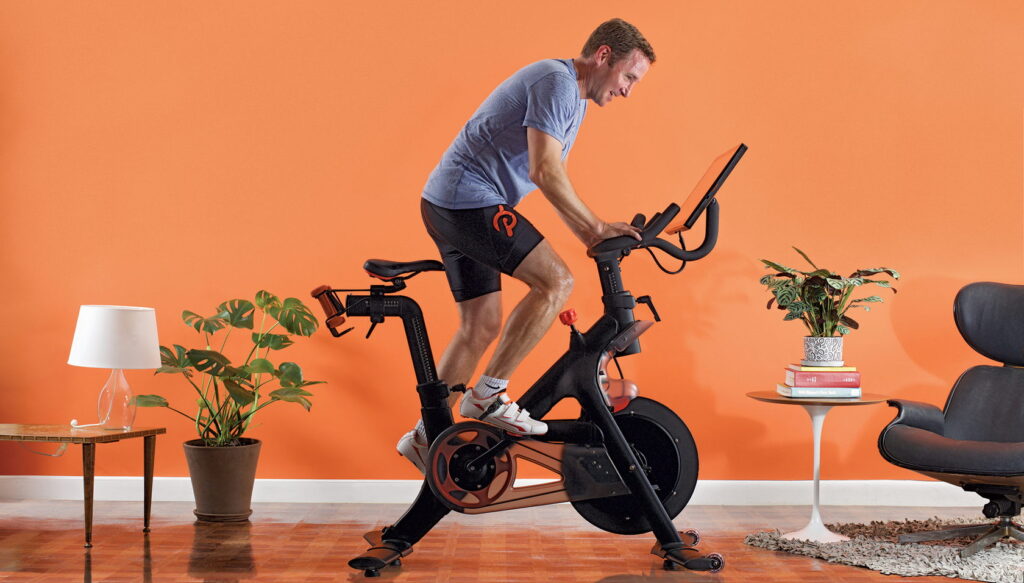
Technically, Peloton is a spin bike. The word “spin” is trademarked, though, but the concept of Peloton seems to be based on spin classes. Peloton bikes have a weighted flywheel like spin bikes do, and with the purchase of a Peloton bike, you have the option to take online spin classes.
The answer to this isn’t a solid yes or no, and it depends on the capabilities and features that your stationary bike has. Spinning is categorized by three different positions, and for all, your feet need to be flat, tightly in the stirrups, with your thighs engaged. So, if you have a stationary bike that the height can be adjusted, it’s likely you can do spin on it.
Like most exercise, it’s recommended to take a rest day or two, especially if you’re doing high-intensity workouts. Spinning every day might cause muscle aches or burnout, depending on how you do it. If you’re only doing it for 15 to 20 minutes per day, there isn’t much risk of injury. Many people also like to spin for five to ten minutes as a cardio warmup for the rest of their workout. It’s always better to err on the safe side and give your body time to rest and adjust to your exercise regimen, especially if you’re trying to find what works best for you.
Spin bikes and stationary exercise bikes are similar, but not the same thing. For one, spin bikes are much heavier because of their flywheel, so they’re less convenient to move around than a stationary bike is. Spin bikes also work more muscle groups than stationary bikes, that only work the lower part of your body. You can also get a much more intense workout from a spin bike, whereas a stationary exercise bike is considered very low impact. They are both good for cardiovascular health and help to sculpt low muscles, and make for a great workout on their own or as a warmup.





